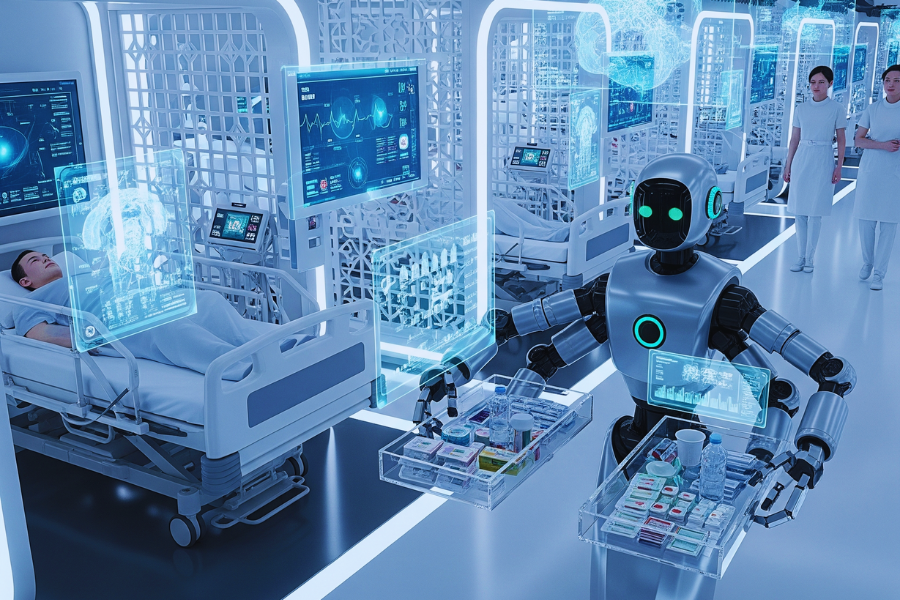
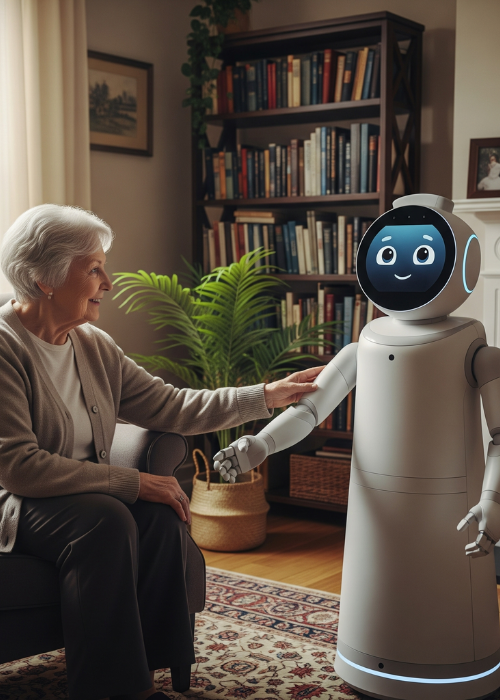
China is rapidly moving beyond the age of industrial automation and stepping into a new frontier—AI-powered robots that don’t just assemble cars or pack boxes but care for people. From hospital wards to retirement homes, prototypes by companies like Dobot and Midea are showcasing how artificial intelligence and robotics can transform healthcare and elder care.
As China’s population ages, with more than 400 million citizens expected to be over 60 by 2035, the need for innovative, scalable, and affordable solutions is urgent. AI bots are emerging as a key answer—capable of performing repetitive tasks, offering companionship, and even assisting in rehabilitation therapies.
The Rise of Caregiving Robots
Unlike factory robots that prioritize speed and precision, healthcare and elder care robots focus on empathy, safety, and reliability. Prototypes from Dobot, known for its collaborative robotic arms, are now being adapted for delicate hospital tasks like medicine dispensing, patient monitoring, and even rehabilitation exercises.
Meanwhile, Midea Group, a household appliance giant, is venturing into elder care with smart robots designed to assist seniors at home. These robots are built to recognize voices, monitor vital signs, and even detect emergencies such as falls.
What’s driving this boom is not only technology, but also social necessity. With China facing a shrinking workforce and ballooning elderly population, AI bots are seen as a lifeline to sustain quality care at scale.
Why China Leads in Healthcare Robotics
China’s leadership in this field comes from a combination of necessity and policy support.
Demographic Pressure: With one of the fastest-aging populations in the world, the demand for robotic caregivers is surging.
Government Investment: Robotics and AI are priority sectors under China’s Made in China 2025 strategy, with elder care tech specifically incentivized.
Tech-Ecosystem Advantage: Companies like Dobot and Midea leverage existing strengths in robotics, AI, and consumer appliances to create practical caregiving solutions.
Cost Innovation: Just as with humanoid robots, Chinese firms are focused on making healthcare bots affordable enough for wide adoption—something Western markets often struggle with.
Challenges & Concerns
Despite the promise, AI bots in healthcare raise several challenges:
Human Touch: Machines cannot fully replace the empathy and intuition of human caregivers.
Privacy Risks: Constant monitoring means sensitive health data could be exposed if systems aren’t secure.
Acceptance: Elderly individuals may find it difficult to trust or adapt to robots in their daily lives.
Regulation: Standards around safety, medical certification, and accountability are still evolving.
Balancing efficiency with ethical and emotional needs will be key for the sustainable adoption of care robots.
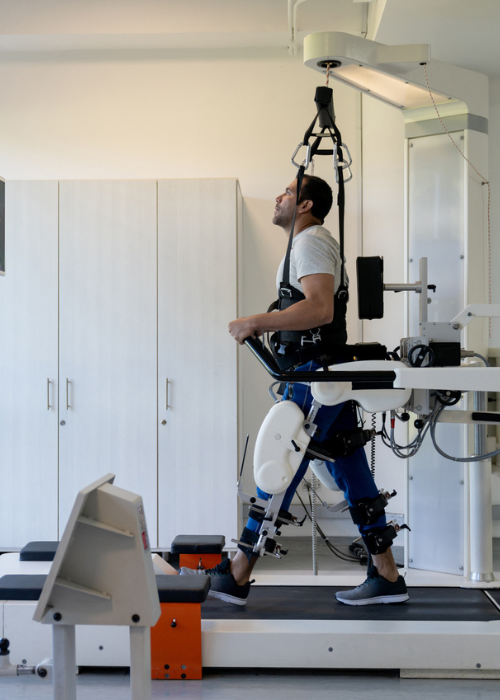

Challenges and Concerns
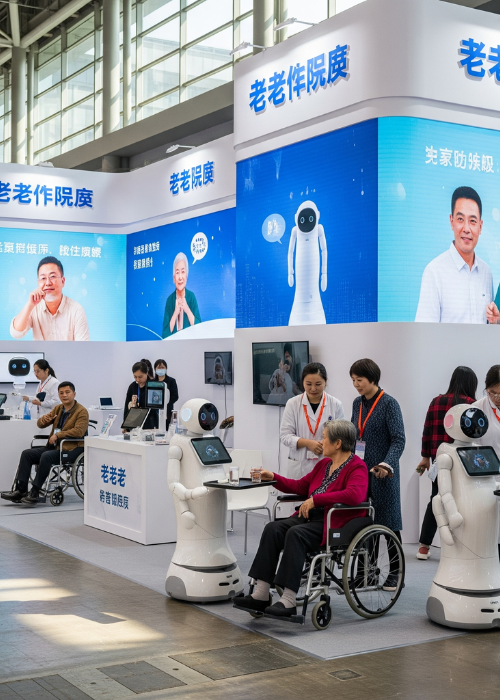

But dark factories aren’t without hurdles.
High Setup Costs: Building a fully automated facility requires massive upfront investment.
Job Displacement: Workers risk losing employment opportunities as machines replace human labor.
Complex Maintenance: Machines still need skilled engineers to manage breakdowns and updates.
Cybersecurity Risks: As factories become connected through IoT, they are more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Ethical Questions: Should societies prioritize cost efficiency over jobs? How do we reskill workers for the AI-driven economy?
The Future: Hybrid Human-Robot Care
Experts believe the future of healthcare and elder care will be a hybrid model: robots handling routine and repetitive tasks, while human professionals provide empathy, judgment, and complex medical interventions.
In the coming years, we can expect:
Smarter Robots with advanced natural language processing for seamless communication.
Integration with Smart Homes so robots can link with IoT devices, wearables, and healthcare platforms.
Affordable Mass Adoption, as costs drop and production scales up.
International Expansion, with China exporting its elder care solutions to other aging societies like Japan and Europe.
Conclusion
China’s push into AI-powered healthcare and elder care robotics is more than a technological trend—it’s a societal response to one of the country’s greatest challenges. With companies like Dobot and Midea leading the charge, robots are stepping out of factories and into our hospitals, clinics, and homes.
They may never replace human caregivers, but as helpers, monitors, and companions, they could redefine what compassionate care looks like in the 21st century.