Introduction
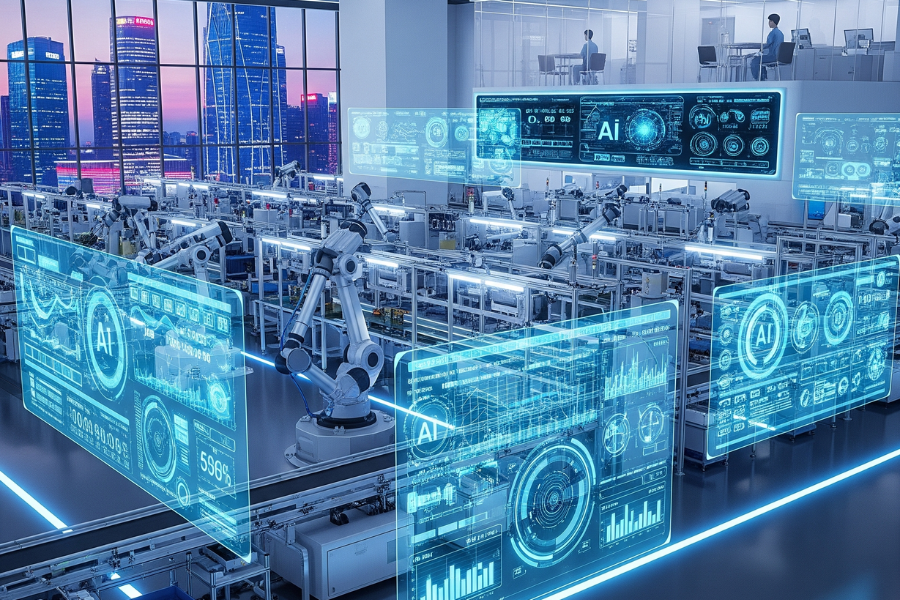
The manufacturing world is entering a new era—Industry 4.0, a transformation defined by smart factories, advanced robotics, and connected systems. At the heart of this revolution are AI agents: intelligent software and hardware systems that can analyze, learn, and make autonomous decisions.
Unlike traditional automation, which follows rigid, pre-programmed steps, AI agents bring flexibility and adaptability to the production floor. They are reshaping how factories operate, how supply chains respond, and how companies compete globally.
Nowhere is this transformation more visible than in China, where AI-driven smart factories are becoming the backbone of modern industry.
What Are AI Agents in Industry 4.0?
AI agents are digital entities powered by machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. In a manufacturing context, they act as intelligent “decision-makers” that can:
Monitor production processes in real-time.
Predict machine failures before they happen.
Adjust workflows automatically to maintain efficiency.
Communicate across networks of machines, suppliers, and logistics partners.
Think of them as the brains of the smart factory, constantly learning and optimizing operations with minimal human input.
Flexibility: Smarter Production Lines
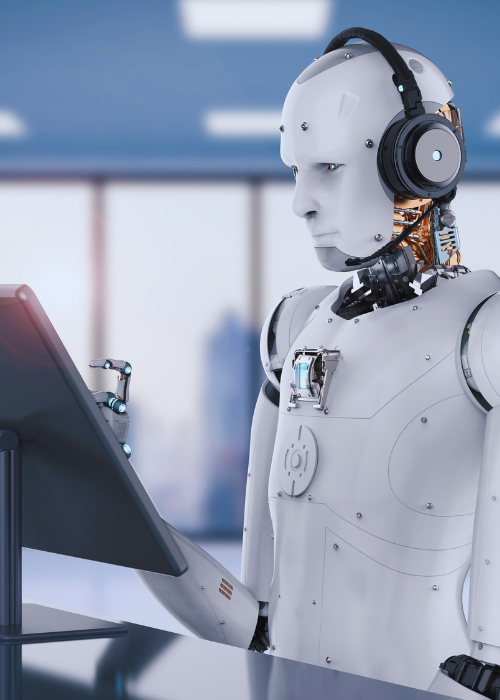

Traditional production lines are designed for mass manufacturing of identical products. Any variation requires costly reprogramming. But consumer demand has shifted—today’s buyers want personalized goods, rapid delivery, and constant innovation.
AI agents enable mass customization by reconfiguring production systems on the fly. For example:
AI scheduling agents can rearrange production sequences to handle smaller, more varied product batches.
Robotic arms guided by AI can adapt to new tasks without needing complete reprogramming.
Digital twins—AI-powered simulations of production lines—help factories test new setups virtually before deploying them physically.
This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond faster to changing market trends while reducing downtime and waste.
Precision: Data-Driven Accuracy
In Industry 4.0, precision is no longer just about machinery tolerances—it’s about data-driven optimization. AI agents use sensor data, IoT devices, and computer vision to detect even the smallest deviations.
Applications include:
Predictive Quality Control: AI systems identify defects in real-time, preventing faulty products from leaving the line.
Smart Assembly: Robots guided by vision-based AI can place components with micron-level accuracy.
Automated Adjustments: Machines can self-correct based on continuous data feedback loops.
This precision not only reduces costs but also builds trust with consumers and global partners, especially in industries like electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
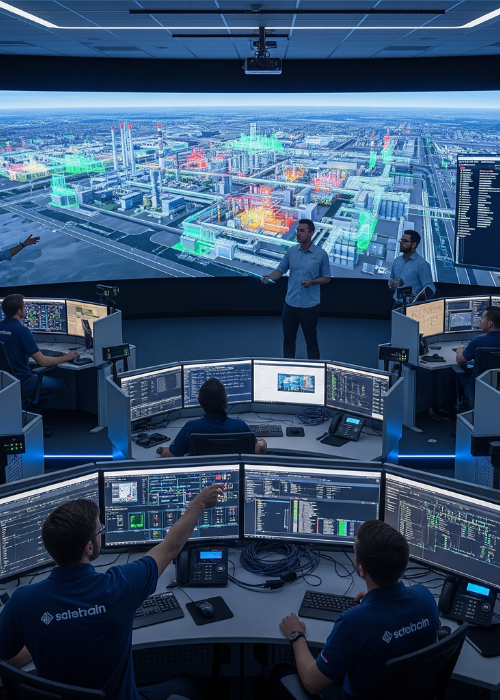

Efficiency: Redefining Productivity
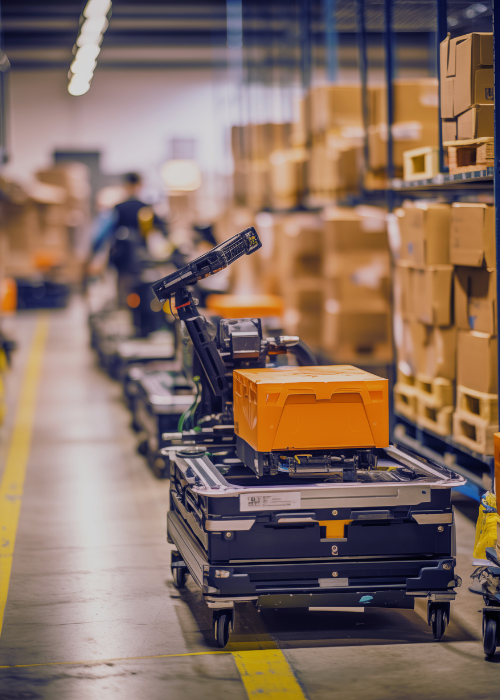

Efficiency in the AI-powered factory is measured not just in speed, but in how well resources are utilized.
AI agents contribute to efficiency by:
Energy Optimization: Adjusting machine cycles to reduce electricity consumption during peak hours.
Supply Chain Synchronization: Predicting material needs and aligning deliveries with production schedules.
Downtime Reduction: Predictive maintenance ensures machines are serviced before breakdowns, extending equipment life.
For example, leading Chinese manufacturers are already reporting double-digit productivity improvements after deploying AI-driven predictive maintenance across smart factories.
China’s Push for AI in Industry 4.0
China has identified Industry 4.0 as a strategic pillar of its economic future. With initiatives like Made in China 2025 and heavy investment in AI research, the country is rapidly scaling smart manufacturing zones.
Foxconn factories have implemented AI-powered predictive maintenance and quality control systems across multiple plants.
Midea Group uses AI scheduling agents to enhance flexibility in its appliance factories.
Huawei’s smart factory solutions integrate AI agents into supply chain logistics and production monitoring.
These moves not only improve competitiveness at home but also position China as a leader in the global automation economy.
The Global Impact
As AI agents mature, their adoption in manufacturing is spreading globally:
Europe: Germany’s automotive industry is using AI agents to optimize assembly and logistics.
United States: AI-powered predictive analytics is being deployed across aerospace and defense sectors.
Asia-Pacific: Countries like South Korea and Japan are focusing on AI-enhanced robotics for precision manufacturing.
China’s aggressive implementation means that global competitors are now racing to keep pace, ensuring that the benefits of Industry 4.0 become a worldwide phenomenon.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promise, challenges remain:
Integration Costs: Smaller firms may struggle with the upfront investment of AI agents and IoT infrastructure.
Cybersecurity Risks: Smart factories are vulnerable to hacking, making security critical.
Workforce Adaptation: Human workers need reskilling to work alongside AI-driven systems.
Ethical Concerns: Increased automation raises questions about job displacement and fair labor practices.
Governments and industry leaders must address these concerns to ensure AI agents contribute to sustainable and inclusive growth.
Conclusion
AI agents are more than just tools—they are partners in production. By enabling flexibility, precision, and efficiency, they are redefining what factories can achieve in the Industry 4.0 era.
China’s rapid adoption demonstrates both the potential and urgency of this shift. For manufacturers worldwide, embracing AI agents isn’t just a competitive advantage—it’s becoming a necessity.
As the line between physical and digital blurs, the question is no longer if AI agents will reshape manufacturing, but how quickly they will define the future of global industry.