Introduction:
The world is reaching the limits of classical computing. Even the most powerful supercomputers cannot solve certain problems in drug discovery, financial modeling, and material science. Enter quantum computing—a technology that uses the bizarre rules of quantum mechanics to process information in ways never before possible.
From China’s 120-qubit quantum computer to global investments worth billions, quantum computing is no longer experimental—it is shaping industries and geopolitics.
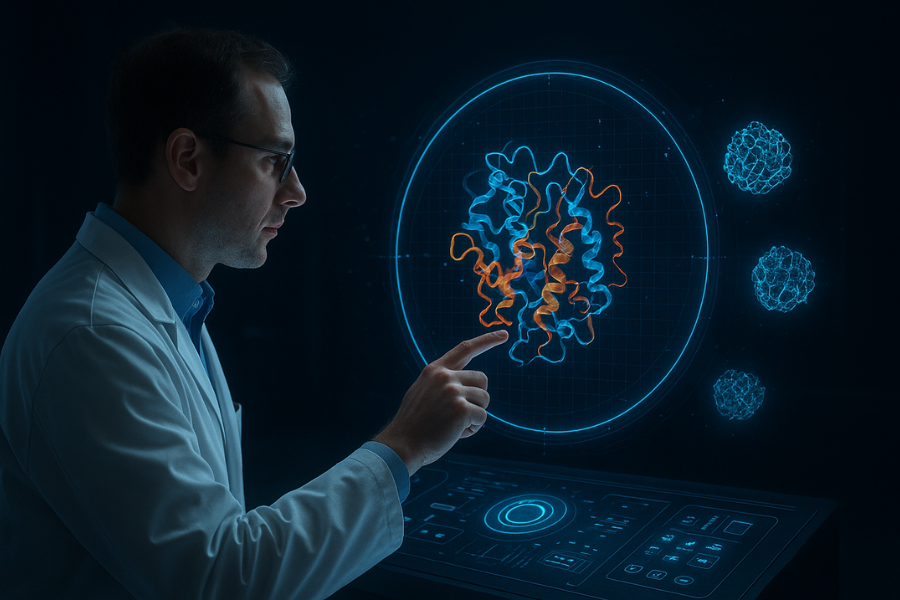
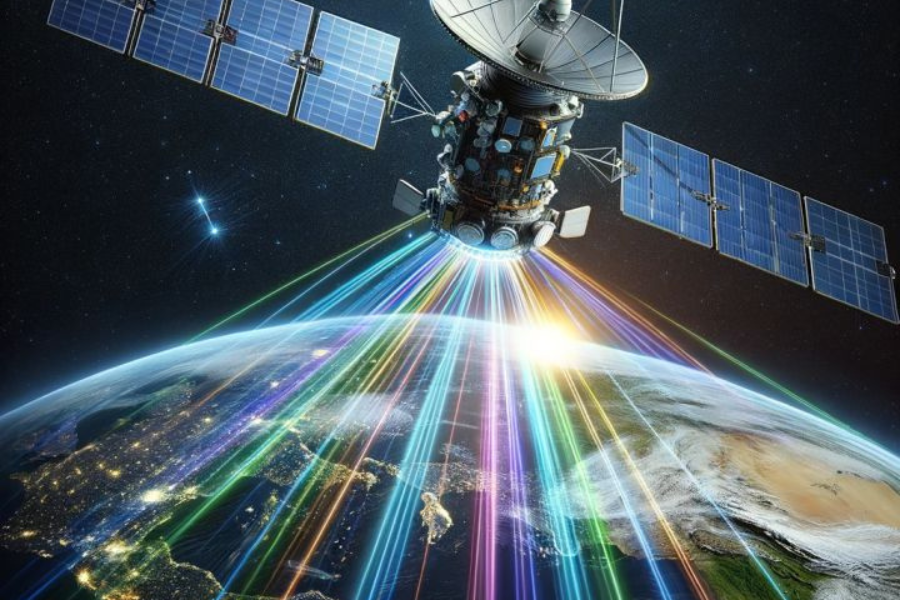



What Makes Quantum Special?
Unlike traditional bits (0 or 1), qubits can exist in multiple states at once (superposition) and link to each other through entanglement. This enables quantum computers to run massive parallel calculations, unlocking solutions impossible for classical machines.
Example: A classical computer might test thousands of possible drug molecules sequentially. A quantum system can analyze them all simultaneously, cutting years of research into days.
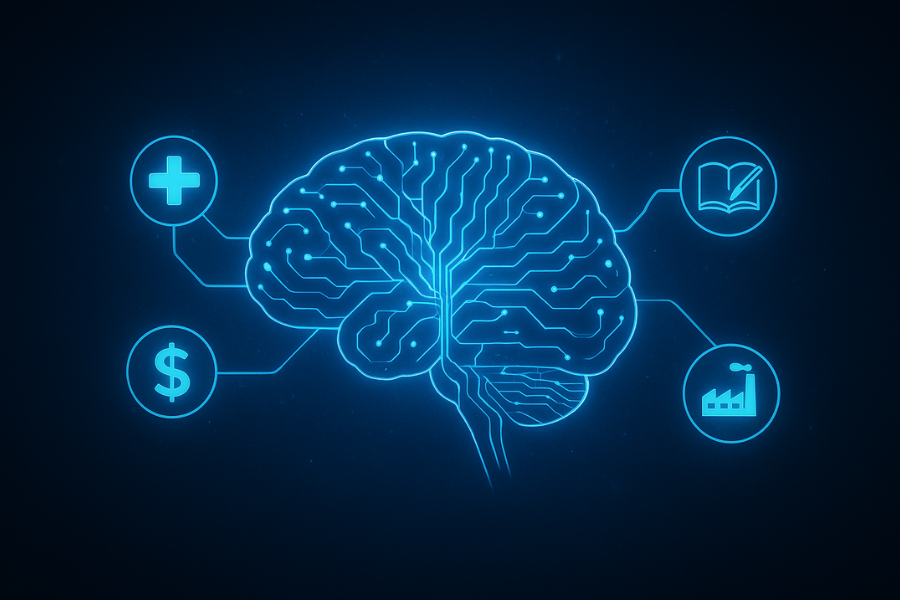
Industries Being Transformed
1. Healthcare & Drug Discovery
Quantum models help simulate complex molecules like proteins and DNA strands, paving the way for treatments against cancer, Alzheimer’s, and rare genetic diseases.
2. Finance & Risk Analysis
Banks experiment with quantum algorithms for portfolio optimization, fraud detection, and high-frequency trading. It helps assess millions of risk scenarios in real time.
3. Energy & Materials
Quantum computing helps design new batteries, superconductors, and solar panels with higher efficiency, accelerating the renewable energy revolution.
4. Cybersecurity
Quantum computers may crack today’s encryption, but they also power quantum-safe communication. China has already launched satellite-based quantum networks—a glimpse into the future of ultra-secure global communication.
Global Race for Quantum Supremacy
Quantum computing is not just science—it’s strategy. Governments and corporations are racing to dominate this technology:
China: Building record-breaking quantum prototypes and secure satellite networks.
United States: Google, IBM, and startups are advancing commercial systems.
Europe & Japan: Heavy investment in quantum hubs and research alliances.
Whichever country leads in quantum could also dominate finance, defense, and digital security in the 21st century.
Challenges Holding It Back
Error Rates – Qubits are fragile and easily disrupted.
Cost & Hardware – Quantum computers need extreme cooling close to absolute zero.
Talent Shortage – Few engineers are skilled in quantum mechanics + AI.
Practical Use – Many algorithms are still experimental, with real-world applications in development.
The Next 10 Years
The future is hybrid computing, where quantum processors work alongside classical supercomputers. Companies like IBM and Huawei envision cloud-based quantum access, letting businesses use quantum without owning the machines.
By the 2030s, we may see:
Quantum-enhanced weather prediction for climate resilience.
Next-gen financial systems built on quantum-safe cryptography.
Widespread medical simulations that save lives faster.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is the crown jewel of cutting-edge technologies. It promises breakthroughs in health, finance, and energy, while also reshaping global security.
The world is on the edge of a quantum leap, and nations that master this technology will define the next century of innovation.

-Futurla