Introduction
Healthcare is one of the most pressing challenges of our time, especially in rural and underserved regions. Limited access to skilled doctors, delayed diagnoses, and resource shortages often mean that patients in villages face far poorer outcomes than their urban counterparts.
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI). With platforms like Alibaba’s ET Medical Brain and other AI-driven diagnostic tools, rural healthcare is being reshaped. These technologies promise faster, more accurate diagnoses, remote consultations, and affordable care, bridging the gap between city hospitals and village clinics.
The Rural Healthcare Challenge
In China, over 500 million people live in rural areas where access to healthcare remains a struggle. Some key challenges include:
Doctor Shortages: Rural clinics often lack trained specialists.
Distance & Delays: Patients travel hours to reach advanced hospitals.
Diagnostic Gaps: Without radiologists or pathologists, many conditions remain undiagnosed.
Costs: Even if services are available, advanced tests are often unaffordable for rural households.
This is where AI-powered diagnostic systems are stepping in as life-changing tools.
Alibaba’s ET Medical Brain: An AI Doctor for All

Alibaba Cloud developed the ET Medical Brain, an AI healthcare platform designed to support hospitals, doctors, and patients with intelligent diagnostics.
Key Features:
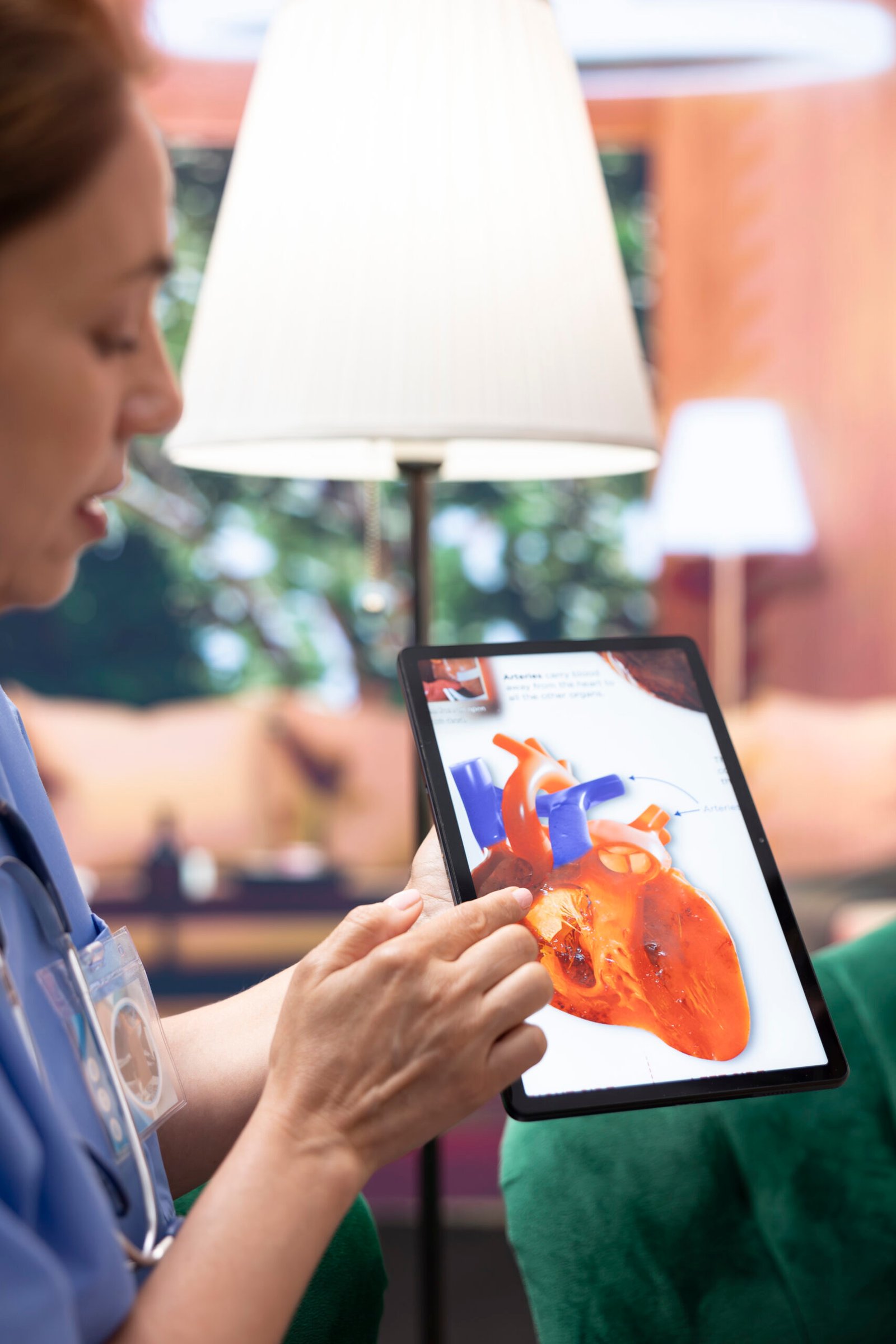
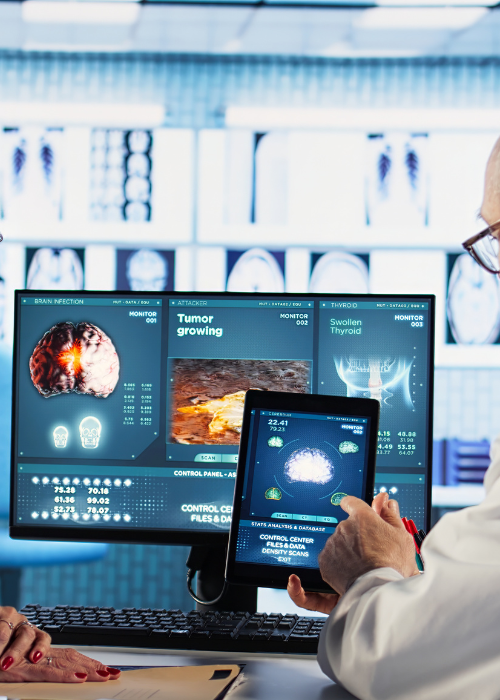
Medical Imaging AI: The system can analyze CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays for diseases like lung cancer, strokes, and tumors with high accuracy.
Assisted Diagnosis: Provides recommendations to doctors, helping non-specialists make expert-level decisions.
Early Detection: Identifies patterns invisible to the human eye, enabling earlier intervention for critical diseases.
Cloud Access: Rural clinics can connect to Alibaba’s cloud platform and get instant AI diagnostic support without needing on-site experts.
This means that a small village clinic, with only basic equipment, can access world-class AI diagnostics in seconds.
How AI Bridges Rural-Urban Divide
Remote Radiology
A rural patient’s CT scan can be uploaded via cloud to the AI system. Within minutes, the algorithm detects possible abnormalities and sends the result back.Decision Support for Local Doctors
Many rural doctors are general practitioners, not specialists. AI provides a “second opinion”, helping them avoid misdiagnosis.Lower Costs
Instead of expensive trips to urban hospitals, patients can be diagnosed locally at a fraction of the cost.Continuous Learning
AI platforms are trained on millions of medical records and images. Every scan improves the system, ensuring rural areas benefit from cutting-edge medicine.

Beyond Alibaba: Other AI Tools in Rural Health

While Ant Group dominates mobile payments and wealth services, Tencent (the parent of WeChat) has leveraged AI to integrate finance directly into daily life.
WeChat Pay Credit Services: Tencent uses AI-driven scoring to assess lending risk for microloans and small business financing.
AI Risk Control: Its fraud detection algorithms analyze billions of WeChat transactions to detect unusual activity in milliseconds.
Wealth Management Chatbots: Tencent’s apps feature AI assistants that guide users through investment options in natural language.
Tencent’s power lies in seamless integration—users don’t need to open a finance app; their financial ecosystem lives inside the same app they use for chatting, shopping, and entertainment.
Success Stories in Rural China
Lung Cancer Detection: In some county hospitals, Alibaba’s Medical Brain identified early-stage lung nodules that even human doctors overlooked. This led to earlier surgeries and higher survival rates.
Stroke Care: Fast detection of brain hemorrhages in remote clinics has enabled timely referrals, preventing long-term disabilities.
COVID-19 Support: During the pandemic, AI helped rural hospitals analyze chest scans, speeding up triage and treatment.
Challenges & Ethical Questions
While promising, AI healthcare faces hurdles:
Data Privacy: Patient data must be protected when uploaded to cloud platforms.
Over-Reliance on AI: Doctors may lean too heavily on algorithms, potentially overlooking human judgment.
Infrastructure Needs: Reliable internet and imaging equipment are still scarce in some rural areas.
Trust Factor: Patients may be hesitant to trust an “AI doctor” without human reassurance.
Governments and tech giants are working to balance innovation with ethics to ensure AI healthcare is safe and reliable.
Global Implications
China’s experiments in rural AI healthcare are being closely watched by other developing nations. Countries in Africa, South Asia, and Latin America with large rural populations face similar healthcare access issues.
If successful, China’s model could serve as a blueprint for global health equity, powered by AI.
Conclusion
The rise of AI diagnostics in rural health is more than a technological advancement—it’s a social revolution. Platforms like Alibaba’s ET Medical Brain are not just scanning images; they are saving lives, reducing inequalities, and ensuring healthcare reaches even the most remote corners of the country.
As AI continues to evolve, the vision of a world where quality healthcare is a universal right, not a privilege, is becoming a reality.