Why Quantum Matters Now
Quantum technology is no longer just theoretical—it’s entering real-world use. Breakthroughs by Google, IBM, the UK government, and the U.S. Department of Defense show strong momentum toward full-scale quantum computing. At the same time, China and Europe are accelerating research, investing heavily in infrastructure and talent.
One area driving this revolution is photonics: by integrating quantum systems onto silicon chips, researchers are opening the door to scalable, secure quantum devices. This combination of advanced computing and light-based engineering could define the next digital era.
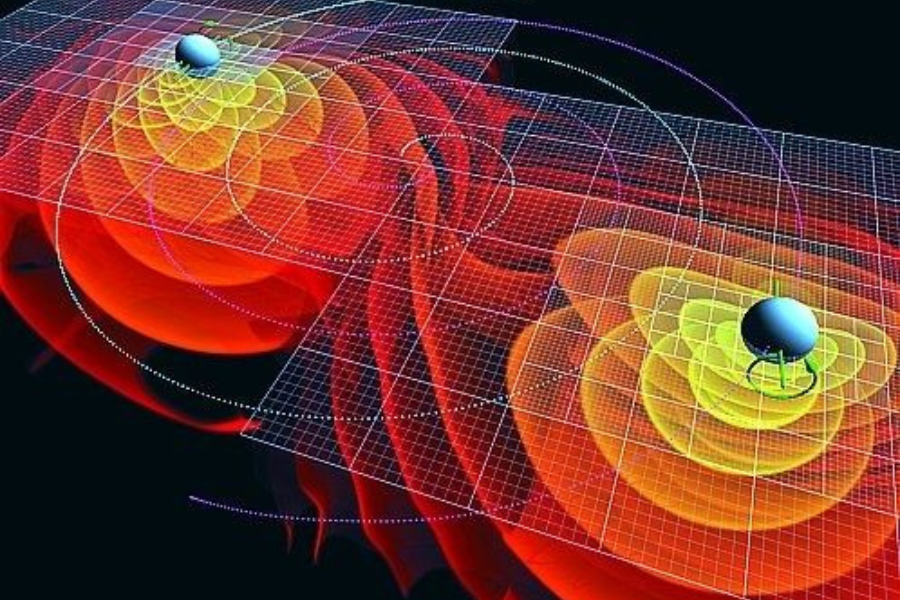


The Quantum Leap: From Physics to Practice
Quantum computing operates on qubits, which leverage superposition (being in multiple states at once) and entanglement (linking particles across distance). These principles allow quantum machines to perform calculations impossible for classical computers.
Global progress: Google’s Sycamore chip, IBM’s quantum roadmaps, and China’s Zuchongzhi processor show that the “quantum supremacy” milestone has been reached in specialized tasks.
Defense interest: National security agencies see quantum as critical for encryption, simulation, and intelligence (Financial Times, TechRadar).
Transformative areas:
Cryptography – Quantum threatens RSA & ECC encryption.
Drug Discovery – Molecular simulations at unprecedented speeds.
Finance – High-speed risk modeling & portfolio optimization.
Logistics – Complex optimization problems solved near instantly (Codnocode, Kowalskypage, Cogent Infotech).
Quantum’s potential is massive—but so are the challenges.
Photonics on a Chip: A Scalable Path Forward
Traditional quantum systems face scaling barriers. Enter silicon-based photonic chips, which integrate:
Waveguides (to direct photons),
Photon sources,
Detectors,
all on a compact and stable platform (arXiv).
Benefits of photonic quantum chips:
Miniaturization → smaller, portable systems.
Stability → less error-prone compared to superconducting qubits.
Compatibility → works with existing semiconductor fabrication lines, making them easier to mass-produce.
This approach promises a future where quantum power isn’t confined to labs but embedded in data centers, telecom networks, and perhaps even personal devices.
Challenges and Cybersecurity Urgency
The road to practical quantum computing is not smooth:
Engineering barriers: Scaling up reliable qubits, managing decoherence, and building effective error correction (Financial Times).
Quantum hype cycles: Risk of overpromising, as seen in past tech winters.
Cybersecurity risks: A large enough quantum computer could break today’s encryption. Yet, only ~4% of organizations currently have a quantum strategy (TechRadar).
To counter this, governments and businesses are now investing in post-quantum cryptography—new encryption systems designed to withstand quantum attacks. China’s Beijing–Shanghai quantum-secure network is a prime example of preparing early.
Looking Ahead: Preparing for the 2020s and Beyond
By the late 2020s, we can expect:
Operational quantum systems in finance, logistics, and defense.
Quantum-safe encryption standards deployed globally.
Quantum workforce growth: Governments and companies investing in talent pipelines.
Strategic adoption in sensitive sectors like healthcare, aerospace, and cybersecurity (Financial Times, TechRadar).
The call to action is clear: governments, universities, and businesses must invest now in quantum literacy, R&D partnerships, and cybersecurity strategies. The race is global, but its impact will touch every industry and every individual.
Conclusion
Quantum technologies are no longer distant dreams—they are rapidly becoming a defining force of the 21st century. From Google and IBM’s experiments to China’s photonic breakthroughs and global investments in cybersecurity, the race toward scalable quantum systems is reshaping science, industry, and geopolitics. While challenges in error correction, cost, and governance remain, the progress of the past few years proves that the quantum era is closer than many expected.
The message is clear: organizations must prepare now—by adopting post-quantum security, building research partnerships, and investing in quantum-ready talent. Those who act early will not only safeguard themselves from risks but also unlock new opportunities in healthcare, finance, logistics, and beyond.
Quantum computing is more than a technology; it’s the next digital revolution—and its future is being written today.

-Futurla